Female Specific Cancer Facts & Symptoms
Some of the cancers that most often affect women are breast, colon, endometrial, lung, cervical, skin, and ovarian cancers. Knowing about these cancers and what you can do to help prevent them or how to find them early (when they are small and easier to treat) may help save your life.

Breast
Breast cancer is the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells that originate in the breast. In West Virginia alone, breast cancer makes up almost 30% of all female cancers.
In the U.S., breast cancer is the second most common type of cancer among women after skin cancer. It can occur in both men and women, but it is rare in men.
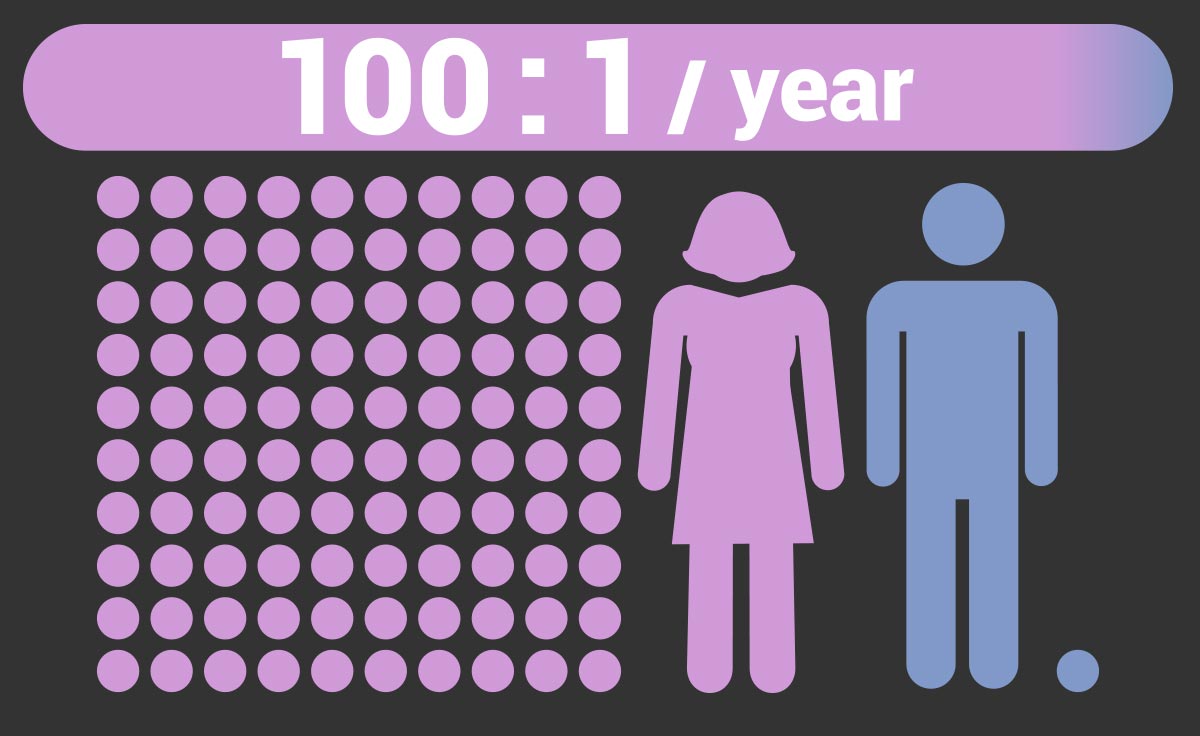
Each year, there are about 100 times more new cases of breast cancer in women than men.
Getting a routine breast screening is the best way to lower your risk of breast cancer. If found, breast cancer can be treated the most effective way at an early stage.

Ovarian
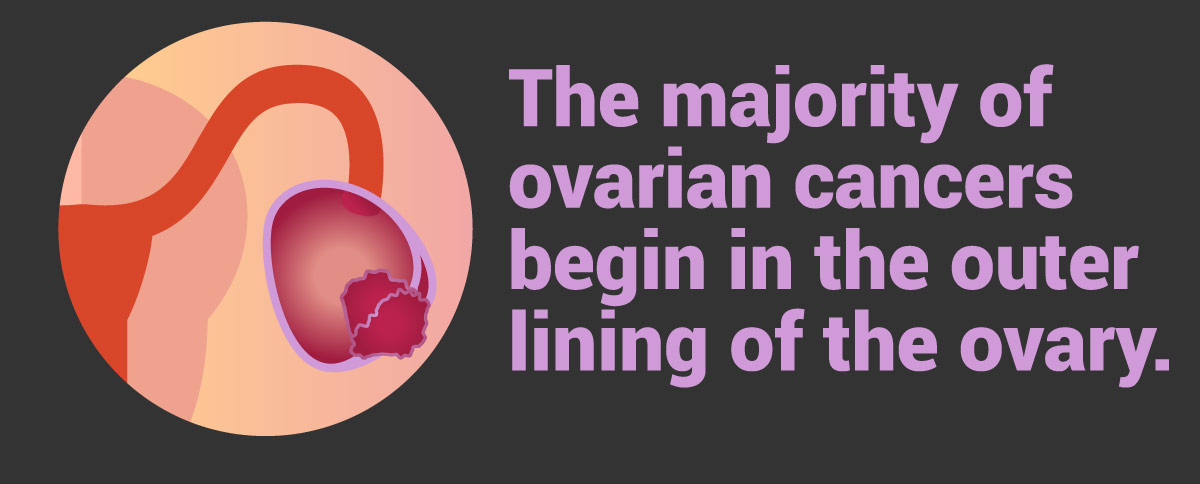
Ovarian cancer is any cancerous growth that occurs in the ovaries, which are part of the female reproductive system. The majority of ovarian cancers begin in the outer lining of the ovary.
Though it is uncommon, ovarian cancer causes more deaths than any other female reproductive cancers, so early detection is crucial.
Common Symptoms of Ovarian Cancer:
- Feeling of heaviness in the pelvis
- Pain in the lower abdomen
- Bleeding
- Abnormal periods
- Back pain
- Gas
- Vomiting
- Loss of appetite
Women with ovarian cancer may experience no symptoms. If they do, the symptoms tend to be mild until the disease has moved to an advanced stage.
Tests for ovarian cancer may include a physical exam, pelvic exam, lab tests, ultrasound, or biopsy. Treatment is usually surgery followed by chemotherapy.
Uterine
Uterine cancer typically begins in the layer of cells that form the lining of the uterus. It usually starts after menopause and occurs most often in women overweight.
Women may also have a higher risk of developing uterine cancer if they took estrogen-only hormone replacement therapy (menopausal hormone therapy) for many years.
Common Symptoms of Uterine Cancer:
- Bleeding between periods
- Trouble urinating
- Pelvic pain and vaginal bleeding after menopause
Tests to find uterine cancer include a pelvic exam, imaging tests, and a biopsy. Hormone therapy, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy are common treatments and sometimes are used in conjunction. However, the most common treatment is a hysterectomy, a surgery to remove the uterus, along with the ovaries and fallopian tubes if needed.

Cervical
Long-lasting infections with certain types of human papillomavirus (HPV) cause almost all cases of cervical cancer. Vaccines that protect against infection with these types of HPV can greatly reduce the risk of cervical cancer.
Cervical cancer testing should start at the age of 21 years old. It can usually be cured if it is found and treated in the early stages.

Having a Pap test to check for abnormal cells in the cervix or a test to check for HPV can find the cells that may form cervical cancer. These cells can be treated before the cancer forms.
Want Alerts and
Helpful Information?

