Lymphatic & Blood Cancer Facts & Symptoms
Lymphoma is a cancer that begins in the lymphatic system, which is part of the immune system. The lymphatic system is composed of lymph nodes in your neck, armpits, groin, chest, and abdomen. It is responsible for removing excess fluids from your body as well as producing immune cells.
Researchers project 61,090 new cases of leukemia in 2021.

Abnormal lymphocytes, a type of white blood cells that fight infection, become lymphoma cells, which multiply and collect in your lymph nodes.
Hodgkin Disease and Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma
About half of the blood cancers that occur each year are lymphomas. Lymphomas are divided into two categories: Hodgkin lymphoma and non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
About 12% of people with lymphoma have Hodgkin lymphoma.
The primary difference between Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin lymphomas can be determined during a biopsy of the affected lymph node. If Reed-Sternberg cells are found in the biopsy – mutated B lymphocytes up to fives times larger than normal – the patient is diagnosed with Hodgkin lymphoma.
Leukemia
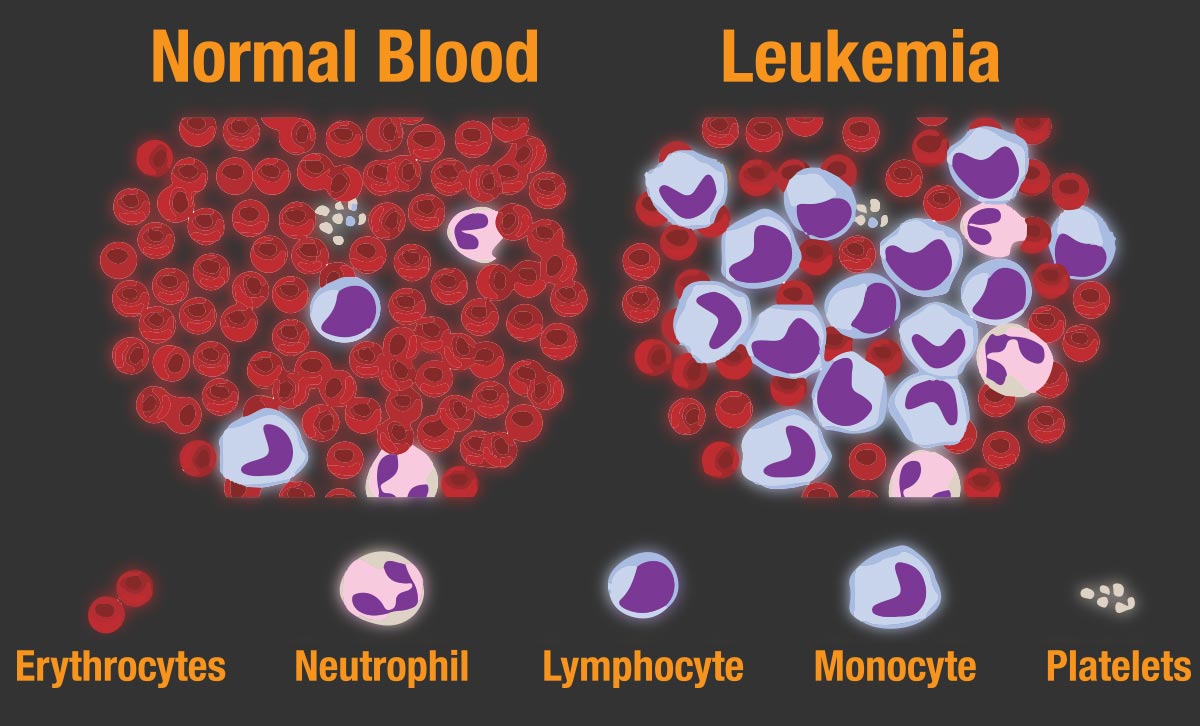
Leukemia is cancer of the body’s blood-forming tissues, including the bone marrow and the lymphatic system, which may be acute or chronic.
Some individuals do not experience symptoms, but rapidly-growing types of leukemia may cause:
- Fatigue
- Weight loss
- Frequent infections
- Easy bleeding or bruising
Before symptoms occur, talk to your doctor about getting screened for leukemia. Additional tests may include lab and imaging for further diagnosis.
Want Alerts and
Helpful Information?

